Build the AI workforce of tomorrow
- Peter Kokkinis
- Mar 17, 2025
- 3 min read
AI Agents: Autonomous Systems for Decision-Making and Problem-Solving
What Are AI Agents?
AI agents are artificial intelligence systems designed to autonomously make decisions, plan actions, and learn from interactions to achieve predefined goals. These systems integrate data from various sources and utilize digital tools to execute tasks efficiently.
Unlike traditional AI models that primarily respond to user inputs, AI agents possess a degree of autonomy. This allows them to tackle complex tasks independently by reasoning, utilizing external tools, and interacting with digital systems in real time to solve multi-step problems.
How AI Agents Function
At the core of AI agents are large language models (LLMs) and machine learning algorithms that enable them to process information, analyze patterns, and generate intelligent responses. By combining language processing with goal-oriented behavior, AI agents can handle tasks dynamically within set parameters.
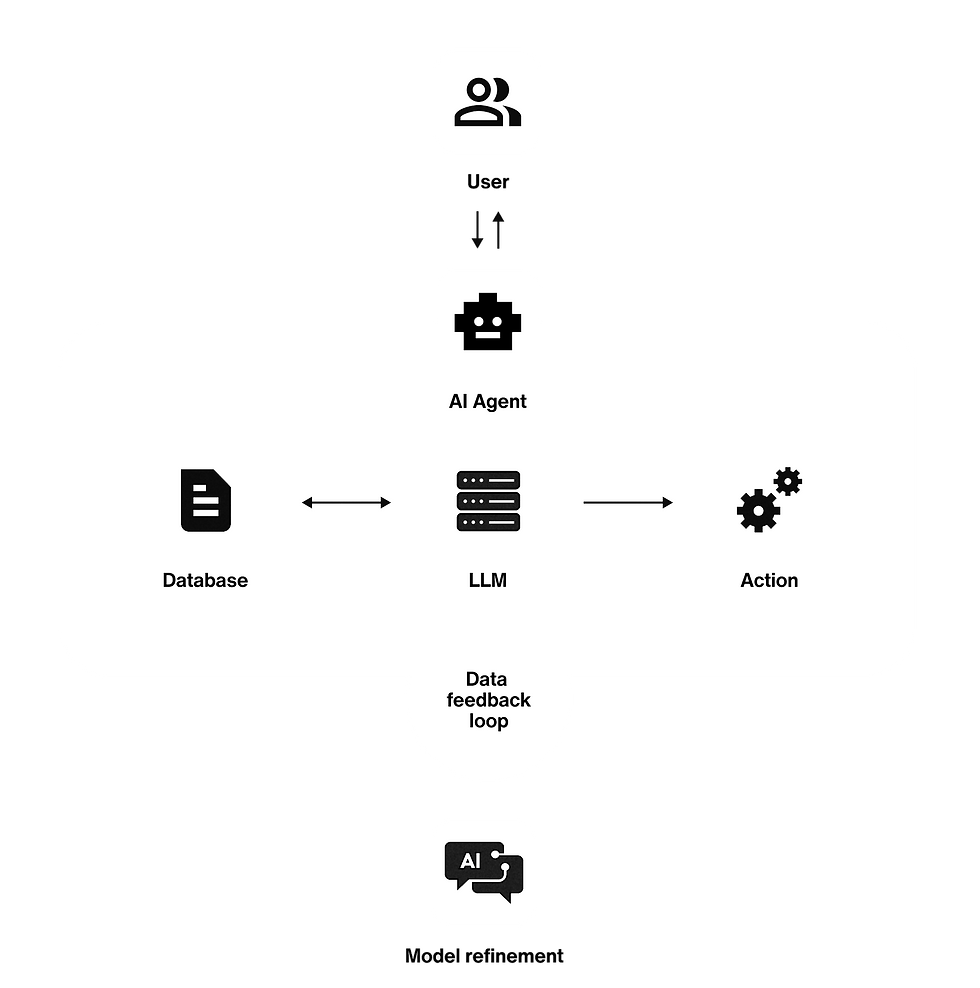
The Four-Step Process of AI Agents:
Perception – AI agents gather data from sources such as customer interactions, databases, IoT devices, and social media. They process and interpret this information in real time to understand their environment.
Reasoning – The system plans actions, determines solutions, and coordinates tasks. It may also retrieve external data sources for enhanced accuracy using techniques like retrieval-augmented generation (RAG).
Action – AI agents execute tasks through APIs and other tools. They can monitor their performance and adjust strategies to improve results while adhering to predefined constraints.
Learning – By analyzing past interactions, AI agents refine their decision-making processes and enhance their performance over time through continuous feedback loops.
Human-Defined Goals and Environments
While AI agents operate autonomously, their objectives and operational scope are determined by humans. The effectiveness of these systems depends on:
Developers who design and train the AI.
Organizations that deploy the AI and configure its access to tools and data.
End-users who assign tasks and define operational constraints.
The environment in which an AI agent functions consists of the systems, data sources, and contextual parameters it is programmed to interact with.
Key Benefits of AI Agents
AI agents are transforming industries by enhancing efficiency, decision-making, and customer experiences. Some notable advantages include:
Autonomy – AI agents can pursue goals with minimal human intervention, optimizing strategies dynamically.
Advanced Problem-Solving – By leveraging AI-driven reasoning, these systems can break down and solve complex, multi-step challenges.
Adaptability – AI agents adjust to new data and evolving conditions, improving responsiveness and effectiveness over time.
Scalability – Modular architecture allows for easy expansion without disrupting existing operations.
Personalization – AI agents analyze past interactions to deliver customized responses and recommendations.
Workflow Optimization – These systems enhance productivity by streamlining processes, managing tasks, and optimizing resource allocation.
Improved Human Interaction – AI-driven natural language processing simplifies communication between users and AI systems.
Enhanced Customer Experience – AI agents anticipate user needs and provide real-time, context-aware solutions to enhance engagement and satisfaction.
Practical Applications of AI Agents
AI agents have the potential to revolutionize multiple sectors by automating complex workflows and enhancing decision-making. Some key applications include:
Business Operations
AI agents can optimize supply chains, manage inventory, coordinate communication, and forecast demand, significantly improving operational efficiency.
Customer Service
By handling routine inquiries and personalizing interactions, AI agents reduce wait times and enhance customer satisfaction while lowering operational costs.
Finance
AI agents can analyze market trends, execute trades, and automate transaction processing, making financial operations more efficient and data-driven.
Cybersecurity
AI agents can detect and respond to security threats in real time, proactively monitoring networks to enhance digital security.
Software Development
Beyond generating code, AI agents can manage development lifecycles, detect bugs, and automate quality assurance, accelerating software production.
Marketing
AI-driven systems can generate content, optimize audience targeting, and analyze campaign performance, improving marketing efficiency and ROI.
The Future of AI Agents
AI agents are set to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of automation, decision-making, and personalized experiences. As these systems continue to evolve, they will further integrate into business operations, customer service, cybersecurity, and beyond, transforming the way industries operate.


Comments